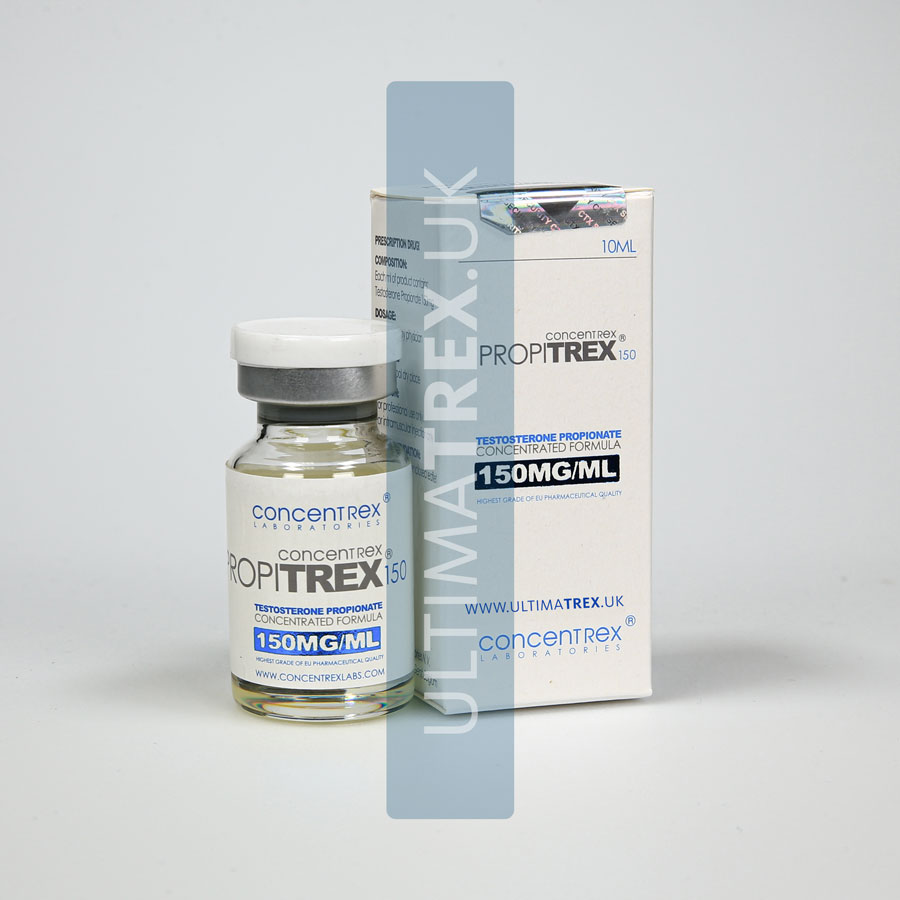
PROPITREX – 150mg/ml
Testosterone Propionate 150mglml 1 VIAL containing 10 mL
For multidose use
Therapeutic Class: Anabolic Agent
Composition:
Each 1 ml of PROPIT REX150 contains:
- 150 mg Testosterone Propionate
- Ethlyl Oleate q.s.
Indication & Dosage:
Intramuscular
Male hypogonadism
Adult: 50-400 mg every 2-4 wk for the cypionate;
50-400 mg every 2-4 wk for the enanthate (or an initial dose of 250 mg every 2-3 wk followed by
a maintenance dose every 3-6 wk);
up to 50 mg 2-3 times wkly for the propionate.
Inoperable metastatic breast cancer
Adult: As enanthate: 200-400 mg every 2-4 wk.
Contraindications :
Hypercalcaemia or hypercalciuria, males with breast or prostate carcinoma. Pregnancy and lactation. ·
Special Precautions
Cardiovascular disorders, skeletal metastases, renal or hepatic impairment, epilepsy, migraine, diabetes or other conditions which may be aggravated by fluid retention, eg heart failure. Elderly, prepubertal boys. Monitor signs of virilization (females) and development of priapism or excessive sexual stimulation (males). Periodic haemoglobin, lipid determinations and rectal prostate examination.
Adverse Drug Reactions
Fluid and electrolyte retention; increased vascularity of the skin; hypercalcaemia, impaired glucose tolerance; increased bone growth and skeletal weight; increase LDL cholesterol; ncrease haematocrit and fibrinolytic activity; headache, depression and GI bleeding.
Males: spermatogenesis suppression, priapism, gynaecomastia, prostatic hyperplasia and accelerate growth of malignant prostate neoplasms.
Females: suppression of lactation, ovarian activity and menstruation; virilization, clitoris hypertrophy, increased libido, oily skin, acne, hirsutism, male pattern baldness.
Children: Closure of the epiphyses and stop linear growth in early puberty, symptoms of virilisation. Precocious sexual development, increased frequency of erection in boys, and clitoral enlargement in girls. IM: urticaria, inflammation at lnj site, postinjection induration, furunculosis
Potentially Fatal: Peliosis hepatis, liver toxicity, malignant neoplasm.
Drug Interactions
Enhance activities of ciclosporine, antidiabetics, thyroxine, anticoagulants. Long term use of testosterone may cause resistance to effects of neuromuscular blockers. Enhance fluid retention from corticosteroids.
Lab Interference
May decrease protein bound iodine (PBI) and thyroxine-binding globulin concentrations. May cause a decrease in excretion of creatinine and creatine and increase in excretion of 17-ketosteroids.
Pregnancy Category
Category X: Studies in animals or human beings have demonstrated foetal abnormalities or there is evidence of foetal risk based on human experience or both, and the risk of the use of the drug in pregnant women clearly outweighs any possible benefit.
The drug is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant.
Mechanism of Action
Testosterone is the principal endogenous androgen responsible for promoting the growth and development of male sexual organs and maintaining secondary sex characteristics in androgen-deficient males.
Storage:
Absorption: Absorbed from GI tract, skin, and oral mucosa
Distribution: 80% bound to sex-hormone binding globulin.
Undergo enterohepatic recirculation. Half-life of testosterone: 10 to 100 min.
Metabolism: Hepatic to active and inactive metabolites. Excretion: Excreted via urine as metabolites; and faeces as unchanged drug (6%)
CIMS Class: Androgens & Related Synthetic Drugs ATC Classification: G03BA03 – testosterone; Belongs to the class of 3-oxoandrosten (4) derivative androgens used in androgenic hormone preparations.
Store at room temperature, between 59 and 86 degrees F (15 and 30 degrees C), in a tightly-closed container. Store away from heat, moisture, and light.
Do not store in the bathroom. Keep out of the reach of children and away from pets.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.